Planning at the Portfolio level is a semi-continuous process in the P4 framework, just like budget planning, for example, which is closely linked to Portfolio Planning. The planning process consists of the preparation through the Portfolio refinement and the Portfolio Planning event. The planning process takes place at the level of the Portfolio Backlog elements. These are:
- Application versions (ie products that can be delivered to the customer)
- System versions (ie fully tested, documented and usable versions of system platforms)
- Module versions
Time is often planned in the following sections, according to the principle “the closer, the finer”:
- four quarters / cycles (ie next cycle, C+1, C+2, C+3)
- the following year (either calendar or C+4 to C+7)
- later
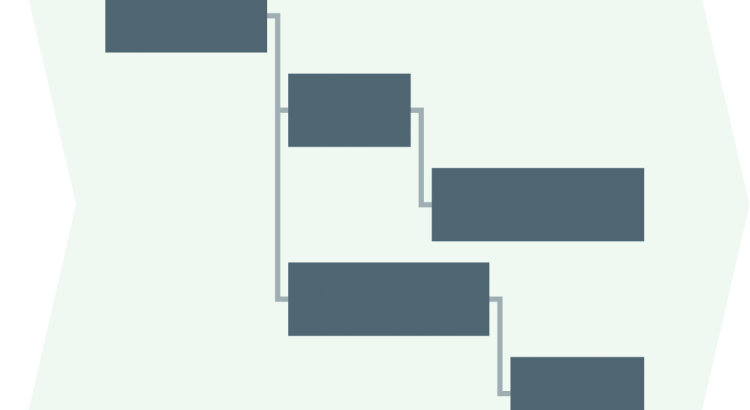
Changes to the Portfolio Planning therefore flow into the Organization well prepared and at certain times. When displayed on a Portfolio Kanban board, the entire work of the Organization becomes transparent.
Portfolio Cycle planning
Every cycle for the entire Organization begins with the Portfolio Planning. In this, the Portfolio Owner (PFO) of the Cluster System Engineer Group (CSEG) presents the current status of the Portfolio Backlog . New entries or changes that have not yet been known to the Cluster System Engineer Group since the last Portfolio Backlog Refinement are estimated, supplemented by Acceptance Criteria and prioritized by the Portfolio Owner within the Portfolio Backlog.
The Cluster System Engineer Group determines the capacity for the next Cycle by looking at the previous “working speed” of the Organization (organizational Velocity) and by looking at the capacity of the Clusters in the next cycle.
The Cluster System Engineer Group pulls the number of Portfolio Backlog Items (PFBI), which corresponds to the CSEG’s assessment of the capacity in the next cycle, into the Cycle Backlog of the Organization (pull). The Cluster Product Owners then use the CSEG to refine the PFBIs into Cluster Backlog Items that are required to complete the PFBIs.
Then the CSEG starts the Cycle by pulling the first items from the “open” to “in progress” state.
Alternative: Portfolio Kanban
Alternatively, the entire Portfolio Planning can also be carried out continuously using a Kanban system. The Cycle as a timebox and the Velocity as a measure of the working speed are omitted. The continuous Portfolio Planning is then carried out through regular meetings between the CSEG and the Portfolio Owner (usually once per Iteration). The activities “introducing”, “estimating” and prioritizing backlog elements then take place on the basis of individual elements. Backlog elements are pulled on the basis of Work-in-progress limits (WiP limit).
.
Further suitable links:\r\n
Further suitable links: